Aug 01, 2023
Molecular Structure Analysis for Mineral and Inorganic Powder Samples
ED2022-08E
Structure analysis of mineral and inorganic powder sample with XtaLAB Synergy-EDand JEOL SEM-EDS
XtaLAB Synergy-ED is a fully optimized electron diffractometer for microcrystals analysis. The key feature of this product allows molecular structural analysis of mineral and inorganic submicron particles. In addition, energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometers (EDS) provide information on the elemental composition of submicron particles for a detailed analysis of molecular structure.
Electron diffraction structure analysis of inorganic and mineral powder
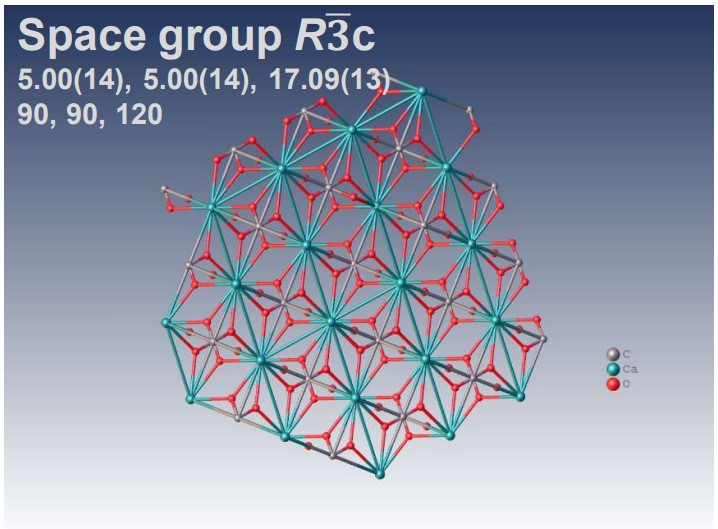
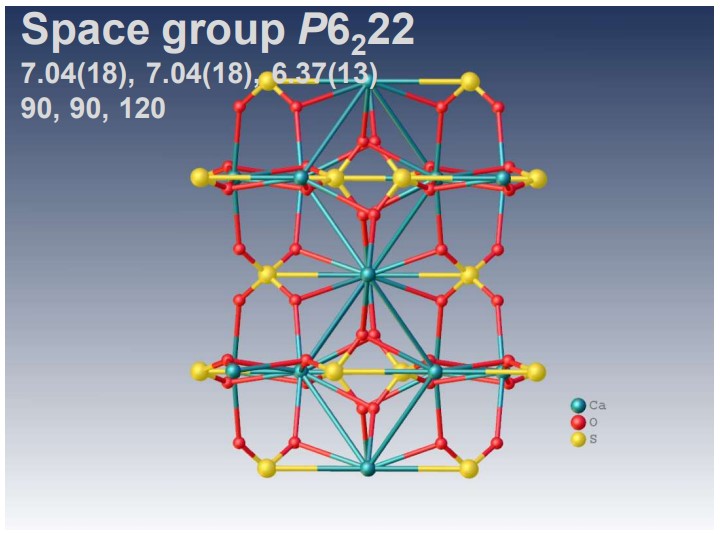
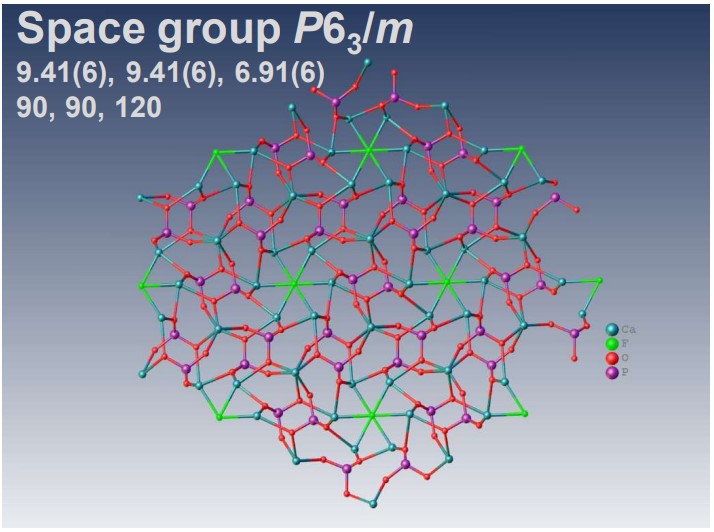
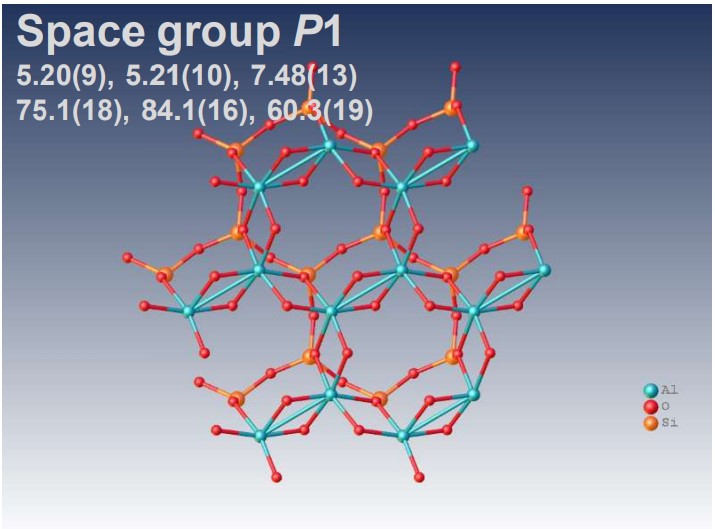
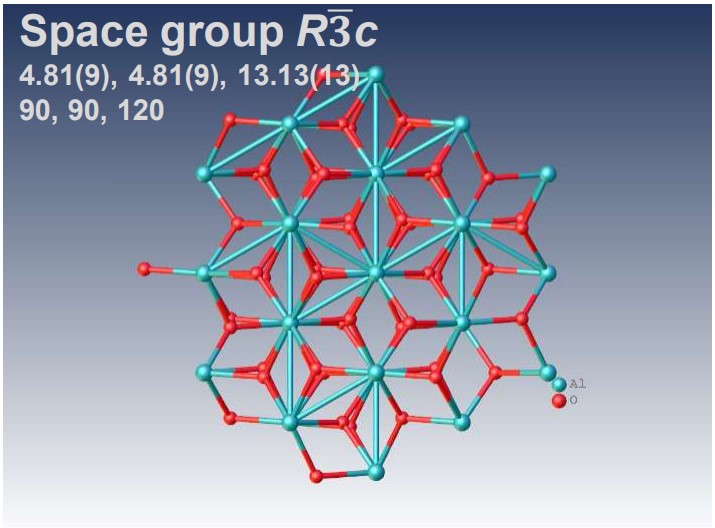
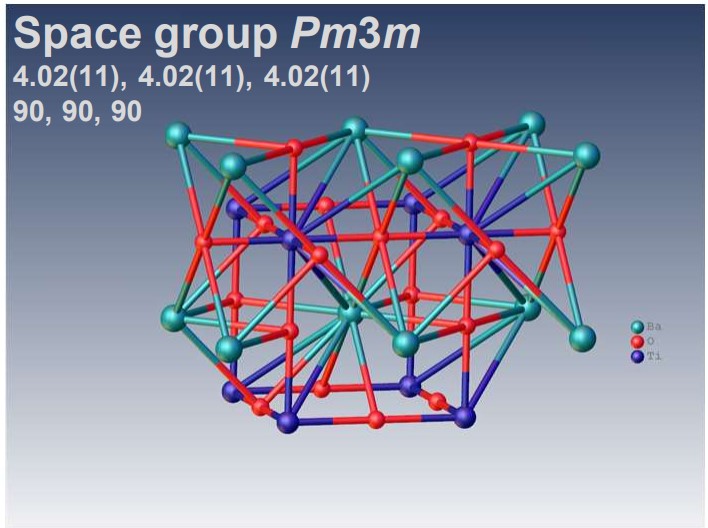
XtaLAB Synergy-ED allows electron diffraction structure analysis of powder samples that can be less than a few μm without any sample preparation. CrysAlisPro for ED is an instrument control with single crystal analysis software platform for 3D ED/microED experiments. This system provides researchers with a simple and effective platform for electron crystallography. The example above shows the results of electron diffraction structure analysis of inorganic and mineral powder samples.
Structure analysis of Kaolinite clay powder
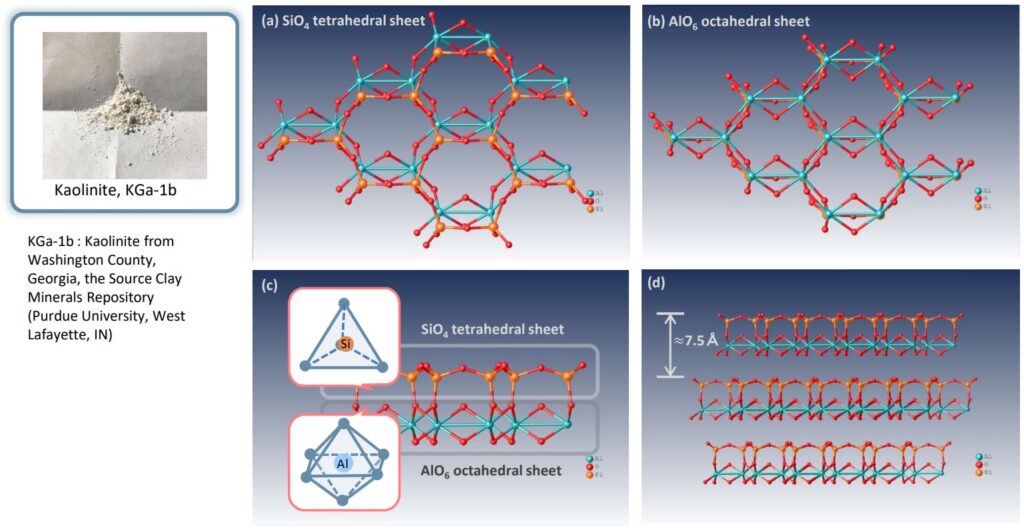
Kaolinite is a clay mineral, produced by the chemical weathering of aluminosilicate minerals like feldspar. This clay is a layered silicate mineral with a silica (SiO4) sheet (a) and an alumina (AlO6) sheet (b). The silica sheet is called T sheet, forms a tetrahedron with each silicon ion surrounded by four oxygen ions and the alumina sheet is called O sheet, and forms an octahedron with each aluminum ion of the alumina sheet surrounded by six oxygen. Both sheets of each layer are strongly bonded together via shared oxygen ions to form a TO layer. Its crystal consists of stacked TO layers, it is described as a fundamental structure of T:O=1:1 clay mineral, Kaolin group (c). The kaolin group serves as important raw materials and has a wide variety of applications for industrial, medical and cosmetic products. Kaolinite, the most well-known 1:1 clay mineral, has many attractive features as a substrate, such as low cost, abundant source, and high mechanical strength. Correctly understanding phyllosilicate materials can provide new applications for diverse functional materials. In the example above, the kaolinite used was KGa-1b from the Source Clay Minerals Repository (Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN), which was used without further purification. Its particle size was less than 2 μm. It is shown that the thickness of the tetrahedral-octahedral layers of the kaolinite is around 7.5 Å (d).
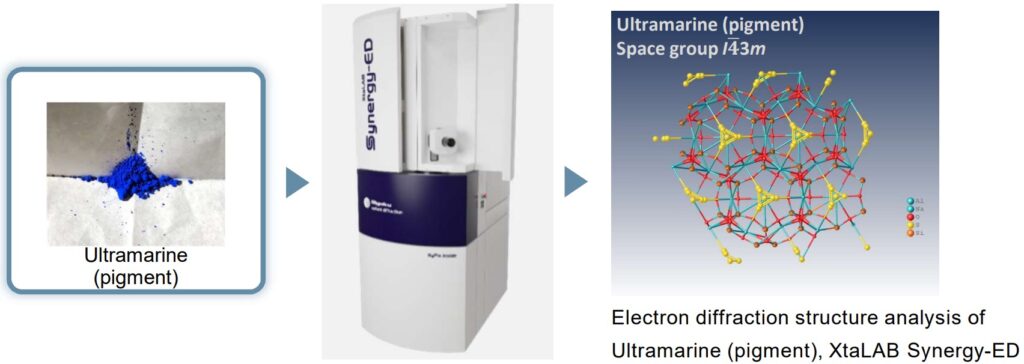
Structure analysis of Ultramarine powder with SEM-EDS and XtaLAB Synergy-ED
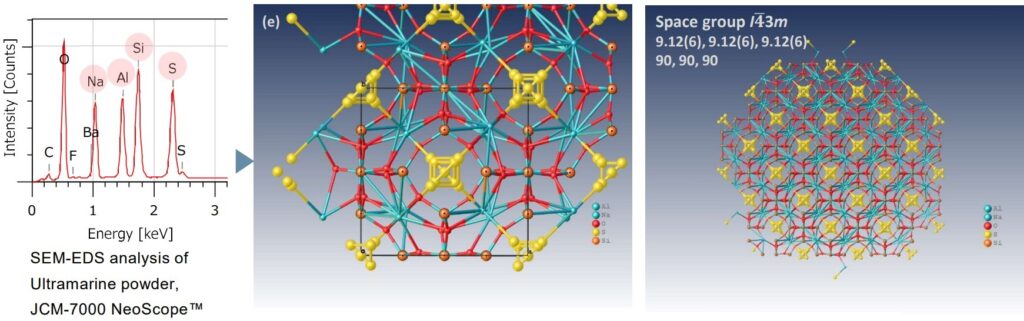
Ultramarine is a deep blue color pigment which is made by grinding lapis lazuli, containing a blue mineral called lazurite, into a powder. In recent years, most of them are synthesized industrially with the major raw materials of Kaolin, anhydrous sodium sulfate. Ultramarine pigment consists primarily of a zeolite-based mineral containing small amounts of polysulfides. The major component of ultramarine is a complex sulfur-containing sodium-silicate, Na8–10Al6Si6O24S2–4, which makes ultramarine the most complex of all mineral pigments. Furthermore, the blue color of the pigment is due to the radical anion S3–. In the example above, the result of elemental composition detected and analyzed by SEM-EDS allows the structure refinement of ultramarine. It is shown that sulfur ions are contained in aluminosilicate cages.
Solutions by field
Environment
Semiconductor and Electronic Parts
Others

